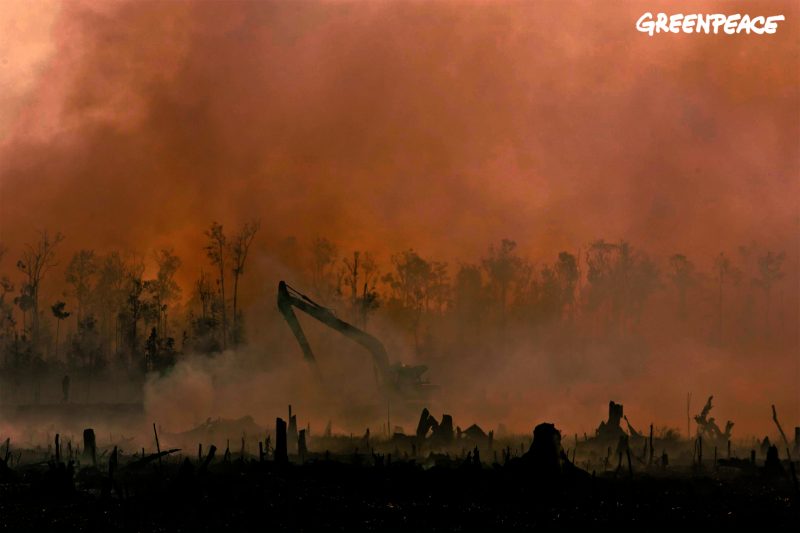
2015 was a devastating year for global greenhouse gas emissions, with Indonesia ranking fourth on the list of top emitters after vast forest fires released 1.62 billion metric tonnes of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Under immense pressure at the UN Climate Change Conference in Paris (COP21) last year, Indonesia announced its commitment to reduce its emissions from peat land fires. Now that a year has passed, do experts believe the government is doing enough to prevent future cataclysmic events from happening?
COP22 ran from November 7 through 18 in Marrakesh, Morocco and was centred on the implementation of the Paris Agreement of 2015. Indonesia’s Minister of Environment and Forestry Siti Nurbaya spoke at the conference about how Indonesia – throughout 2016 – has taken many operational steps and policies that have had a direct impact on the reduction of emissions.
Nurbaya listed Jokowi’s moratorium, the restoration of peat land, the control of forest fires, and the prevention of deforestation as part of the measures being taken to reduce carbon emissions. According to the Minister, these actions have clear indicators that “can be measured, monitored and verified”.
Recent data shows no signs of deforestation slowing down, which is a direct contradiction to Minister Nurbaya’s speech at COP22.
While independent scientific sources indicate a strong increase in deforestation over the last decade, the Ministry of Forestry reported stable deforestation levels and emissions.
Deforestation on the rise
Indonesia’s Intended Nationally Determined Contribution (INDC), released in September last year, includes an unconditional 2030 greenhouse gas emissions reduction target of 29 percent below business-as-usual (BAU) and a conditional 41 percent reduction below BAU by 2030 (with sufficient international support).
In stark contrast, according to independent scientific analysis consortium Climate Action Tracker, “Indonesia is the only main deforesting country where a strong increase in deforestation emissions can be expected in the period to 2030.” The group claims that Indonesia has a contradictory climate policy, where renewables are being pushed to play a stronger role in the energy mix, while a growing demand for coal is leading to continually rising emissions. They predict a 70 percent increase in emissions above the 2010 level by 2030 from energy and industry sectors.
A weak commitment
Environmental activists on the ground believe Indonesia’s commitment is weak and not ambitions enough. Annisa Rahmawati is the Forest Campaigner for Greenpeace Indonesia. She was shocked to hear the government is planning an increase in global greenhouse emissions of around one third by 2030. “Deforestation and peat land destruction accounts for approximately 60 percent of Indonesia’s emissions, but Indonesia’s measures to protect peat lands are insufficient,” she told Indonesia Expat. “The government is even planning 13 million hectares of further deforestation in the next three decades as revealed in the INDC.”
An ineffective moratorium
Jokowi’s moratorium on new palm oil concessions, according to Rahmawati, up until now still has no legal binding form, rendering it useless. “The President’s ban on new developments on peat land seems not to be obeyed by the industry, and the lack of law enforcement has added to its complication,” says Rahmawati. The problem is, “The moratorium is not permanent and doesn’t apply to land where permits have already been granted.” According to Greenpeace, there are approximately 10 million hectares of forest currently under threat in existing oil palm, pulp and mining concessions.
Environmental activist Chanee Kalaweit, who works saving animals in the fire hazard zones of Kalimantan and Sumatra, believes the peat land fire threat is still very much alive. In 2015 Kalaweit became a household name when his video addressed to the president taken from the thick of the forest fire haze in Kalimantan went viral. He believes the only reason we are seeing fewer fires this year is because of the La Niña weatherfront, not because of any measures being taken by the government.
“This year it’s La Niña, which always comes the year after El Niño,” he tells Indonesia Expat. “We are experiencing a lot of rain with no real dry season in Borneo. Next year the dry season will be normal, and every year it will be longer until the next El Niño in 2020/2021,” he warns. Kalaweit believes the next El Niño will be catastrophic in terms of forest fires and Indonesia’s contribution to climate change.
What actions should be taken?
Like Rahmawati, Kalaweit believes the government is not doing enough to prevent further peat land forest fires. He has observed that many landowners are converting their land status to Areal Penggunaan Lain (APL) or Area for Other Uses, which is exempt from the moratorium, allowing them to continue as palm oil plantations. What he believes should be done to prevent further fires is: 1) focus prevention funds on peat land forests only; 2) prepare water pumps at every problem area; 3) forbid any form of fire creation in the dry season in peat land areas, as he says they do in Europe in pine forests. Kalaweit also believes the government must forbid the opening of large-scale land in any APL region.
Both activists believe in order to prevent future fires, the plantation industry must move away from peat lands and start to remedy the damage that has already been done. This can be done through blocking canals and rewetting as a first step to restoring peat lands to their natural condition – an effective measure based on Greenpeace Indonesia’s experience in Riau and Central Kalimantan.
Ambitious plans of bringing together land use, land tenure and other spatial data into a singular incorporated database for Indonesia, known as the One Map initiative, began under the previous government, but has yet to be completed. Rahmawati believes that without transparency of baseline data and methodology, enabling independent monitoring and accurate calculations about what is actually happening on the ground – while understanding who owns the land and who is responsible for fires and environmental destruction – both the moratorium and One Map policy “will be meaningless”.
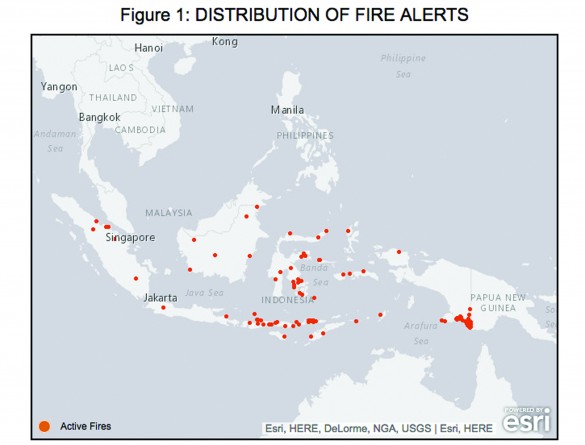
In the length of time it took to write this article, the Global Forest Watch reported that Indonesia received 174 fire alerts (see map). Fourty-two percent of the fires occurred on indicative moratorium areas.




